Imagine driving through the serene countryside, surrounded by rolling agricultural hills, peaceful residential homes, and quaint farmsteads. Suddenly, you stumble upon a colossal building fenced in with security cameras and humming with industrial-scale cooling equipment. You might wonder, “What on earth is that doing here?” Welcome to the world of large language models (LLMs) and the unexpected places they call home.
What is LLM? Large Language Models (LLMs) are at the forefront of artificial intelligence, transforming how machines understand and generate human language. Developed by leading AI companies, these models harness vast data and computational power to perform complex language-related tasks with remarkable precision.
Development and Training: The creation of LLMs involves collecting extensive datasets, which often include text from books, articles, websites, and other sources. This data is crucial for training the models to recognize patterns, understand context, and generate coherent text. Advanced deep learning techniques involve billions of parameters that must be adjusted for optimal performance.
The Birth of Giants: Large Language Models are the new giants in artificial intelligence. These behemoths are trained on vast amounts of data, gobbling up text from books, articles, websites, and more. But teaching these giants is no small feat—it requires industrial-scale infrastructure. Picture buildings that look more at home in an urban industrial park than nestled among cornfields. Yet, these data centers are strategically placed in rural areas, where cheap land and nearby power stations offer the perfect setup for cost-effective operations.
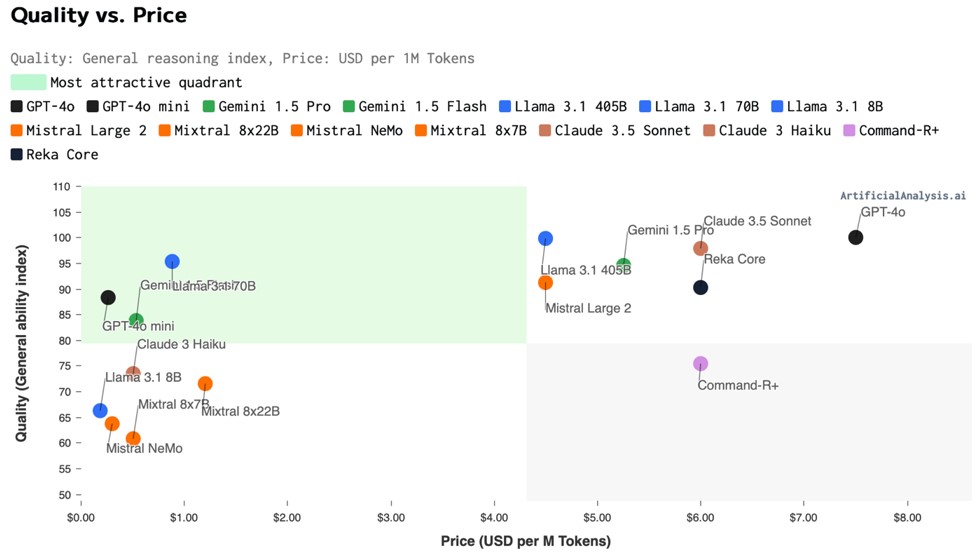
Performance Usually Comes at a Price: One of the most tracked metrics is the overall performance quality measured against the cost to run that model. This is a highly relevant perspective. If a model is fantastic but too expensive to work with for most parties, then it simply won’t scale.
Source: Artificial Analysis
Take GPT-4o, for example, which was released on May 13. It led the pack in terms of performance, closely followed by Anthropic’s Claude 3.5. However, on July 23, Meta released Llama 3.1 405b, matching GPT-4o’s performance but at almost half the operational cost. This breakthrough makes Meta’s Llama 3.1 405b highly competitive, proving that effective AI doesn’t have to break the bank.
The Power and Data Dance: Training an LLM isn’t just about feeding it data; it’s a full-blown orchestration of resources. It takes billions in investment to equip these centers with the necessary graphics processing units (GPUs), servers, racks, cooling systems, cabling, and the buildings to house it all. And let’s not forget the energy—about 100 megawatts of electricity per center. That’s enough to power around 100,000 homes. Multiply that by at least 20, and you have a sense of the colossal scale we’re talking about. It’s like running a mini city, but AI churning out text and insights instead of people.
Farmers and Servers: A Surprising Symbiosis: While finding high-tech data centers among rural landscapes might seem odd, the location makes perfect sense. Cheap land and proximity to power stations are crucial. These centers need enormous power and water to keep everything running smoothly. The rural setting provides precisely that, making it the unlikely but ideal habitat for these digital giants.
The Major Players: In this high-stakes game, seven major players (outside China) dominate the field. Five boast well-established user interfaces—think of them as the friendly faces of AI technology, ready to deliver powerful AI capabilities directly to users. Companies like OpenAI, Google, Microsoft, and Facebook are leading the charge, each contributing unique advancements to the world of LLMs.
However, it’s notable that xAI, spearheaded by Elon Musk, seems conspicuously absent from mainstream discussions. Despite releasing Grok 1.5 on April 12, xAI has faced a lukewarm reception, reminiscent of Tesla’s treatment in the electric car industry, where it often gets overshadowed by other manufacturers like General Motors.
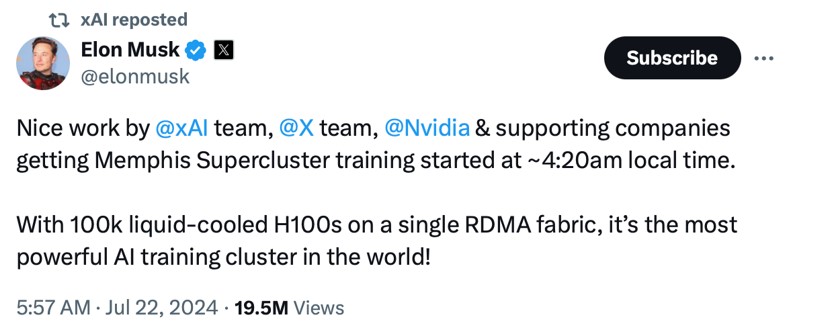
But xAI isn’t going anywhere. It’s a player after having raised $6 billion a few months ago. And just two weeks ago, it started training its next-generation model with enough horsepower to get it done. It has the GPUs…
Agriculture Gets a High-Tech Boost: One of the most exciting applications of LLMs is in agriculture. Imagine AI-driven solutions optimizing crop yields, managing resources efficiently, and transforming farming practices. Sensors in the fields collect data, AI models analyze it in real time, and farmers get precise recommendations on planting and harvesting. All this data is stored in the cloud, making it accessible anytime. It’s a high-tech revolution in the heart of the farmland.
President Trump’s Vision: In a recent speech at Bitcoin 2024, President Trump highlighted the importance of strengthening the electric power industry to make electricity cheaper for American companies. This initiative aims to reduce operational costs for businesses, including those in the tech sector, which rely heavily on electrical power for data centers and computational resources.
Conclusion: The development of Large Language Models represents a significant leap in AI, enabling machines to understand and generate human language with unprecedented accuracy. Major AI companies continue to push the boundaries of this technology, leveraging vast amounts of data and computational power to train and refine these models. The applications of LLMs span various industries, including agriculture, where they are poised to revolutionize farming practices. As the demand for data and computational resources grows, initiatives to make electricity more affordable and sustainable will play a crucial role in supporting the continued advancement of LLM technology. This evolution underscores the opportunities and revolutionary significance brought by LLM predictions, promising a future where AI capabilities are both powerful and accessible.

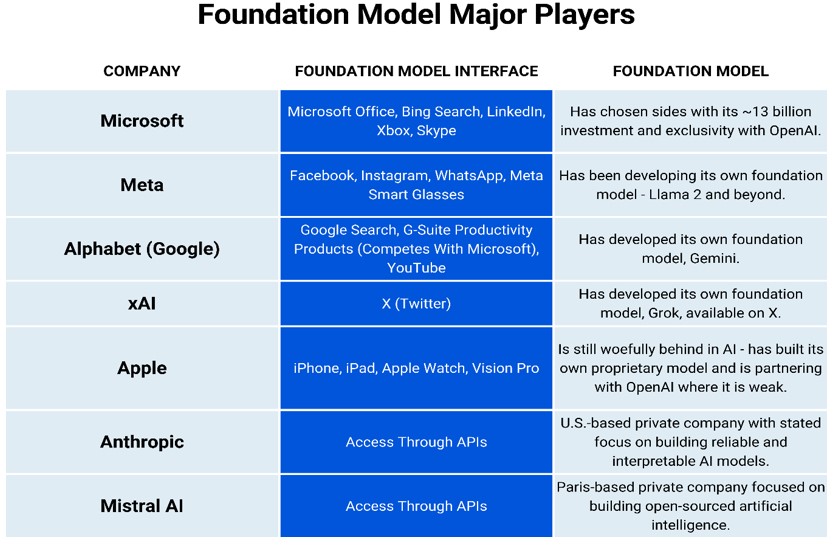
[…] The major players in this competition include Microsoft, OpenAI, Meta, Alphabet (Google), xAI (Elon Musk’s venture), Apple, and Anthropic. But let’s remember the rising star, Mistral AI, which is quickly making its mark. For those who want to dive deeper into the dynamics among these AI titans, I’ve discussed them extensively in The BitVision – AI Titans: Redefining Industries and Pioneering the Future. […]